Above all, we need to know that asymmetric encryption is much slower than symmetric encryption. So, in practice, we usually use them in combination. First, asymmetric encryption is used to exchange a shared key, which is symmetrically encrypted; then, in the subsequent communication, the shared key is used to symmetrically encrypt all messages.
首先,我们需要知道,非对称加密比对称加密要慢的多。所以在实际应用中,通常将二者结合起来使用。先使用非对称加密来交换一个共享密钥,该密钥是对称加密的;然后在后续会话中,使用该共享密钥对数据进行对称加密。
Key Exchange
Key Exchange, in cryptography, refers to the protocol by which two communicating parties exchange a cryptographic key on an open channel. Of course, the key exchange usually does not transmit keys directly on the open channel but rather exchanges certain factors for calculating the key(DH key exchange) or exchanges the key encrypted by a public key(RSA key exchange). Then, both parties will calculate the same key (aka. shared key or shared secret) for the following data encryption transmission.
Common key exchange protocols include RSA, DH, and ECDH.
Key Exchange 密钥交换,在密码学中是指通信双方在公开信道上交换密钥的方式。当然,密钥交换并不是说在公开信道上直接传输密钥,而是交换计算密钥的某些因子(DH 密钥交换),或者是用公钥加密过的密钥(RSA 密钥交换),然后双方再各自计算出这个密钥(通常被叫做共享密钥),用来做后续的数据加密传输。
常见的密钥交换协议有 RSA, DH, ECDH。
RSA Key Exchange
RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm, and its basic principle can be simplified as follows. The selection of the three numbers E, D, and N must meet certain mathematical requirements, which will not be discussed in depth here.
Ciphertext = Plaintextᴱ mod N // RSA encryption, Pubic key={E, N}
Plaintext = Ciphertextᴰ mod N // RSA decryption, Private key={D, N} (结城浩, 2016)Here is a simple example:
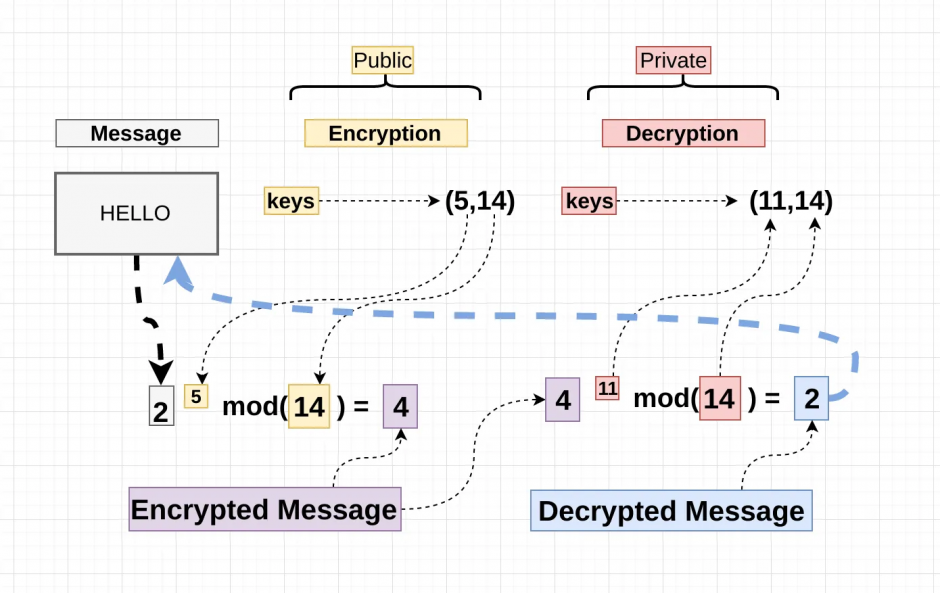
If RSA is used in the key exchange process, the general steps are as follows:
- Bob sends the public key to Alice;
- Alice generates a shared symmetric key, encrypts it, and then sends it to Bob;
- Bob uses his private key to decrypt the shared key;
- Shared key exchange completed.
RSA 是一种非对称加密算法,它的基本原理可以简化成如下形式。其中 E, D, N 三个数字的选择需要满足一定数学条件,这里不做深入讨论。
密文 = 明文ᴱ mod N // RSA 加密, 公钥={E, N}
明文 = 密文ᴰ mod N // RSA 解密, 私钥={D, N} (结城浩, 2016)这里有一个简单的例子:见上图。
如果将 RSA 用在密钥交换过程中,就是
- Bob 将其公钥发送给 Alice;
- Alice 计算出一个共享密钥后,使用 Bob 的公钥加密再发送给 Bob;
- Bob 私用私钥解密后获得共享密钥;
- 密钥交换完成。

Diffie-Hellman(DH) Key Exchange
DH key exchange was the first published public-key algorithm(asymmetric encryption) and was widely used in key exchange.
DH key exchange steps are as follows:
- Agree on public parameters
The two parties (let’s call them Alice and Bob) choose a large prime numberpand a baseg(an integer less thanp, andgis a primitive root modulop) and share them publicly; - Each party generates private keys
• Alice randomly chooses a private keya(1 < a < p);
• Bob also chooses a private keybrandomly (1 < b < p). - Calculate public keys and Exchange public keys
• Alice calculates the public keyA = gᵃ mod p;
• Bob calculates the public keyB = gᵇ mod p
• Alice and Bob send their public keys(A, B)to each other. This exchange can be done over an insecure channel. - Each party computes the shared key
Alice calculates the shared keys = Bᵃ mod p;
Bob calculates the shared keys = Aᵇ mod p;
Due to the properties of mathematics, thesAlice and Bob calculated the same. - Sending messages encrypted by the shared key
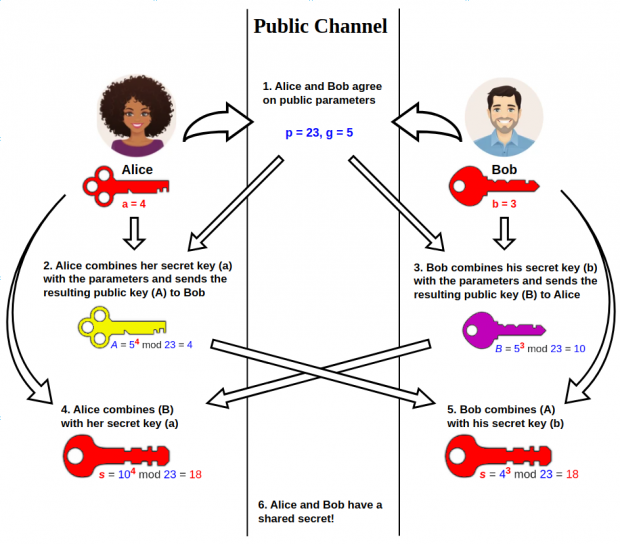
DH 密钥交换步骤:
- 选择公开参数
通信双方(通常称为 Alice 和 Bob)选择一个大型素数p和一个生成元g(通常是小于p的整数,并且g是p的原根 primitive root, 即gⁱ mod p可以生成所有[1, p)之间的的整数),并将这两个数公开; - 生成私有密钥
• Alice 随机选择一个私钥a(1 < a < p).
• Bob 随机选择一个私钥b(1 < b < p). - 计算公钥并交换
• Alice 计算公钥A = gᵃ mod p.
• Bob 计算公钥B = gᵇ mod p.
• 双方公开交换公钥(A, B),这个交换可以在不安全的通道上进行。 - 计算共享密钥
• Alice 计算共享密钥s = Bᵃ mod p;
• Bob 计算共享密钥s = Aᵇ mod p;
• 由于数学的性质,Alice 和 Bob 计算出的 s 是相同的。 - 使用该共享密钥进行消息加密与解密
Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman(ECDH) Key Exchange
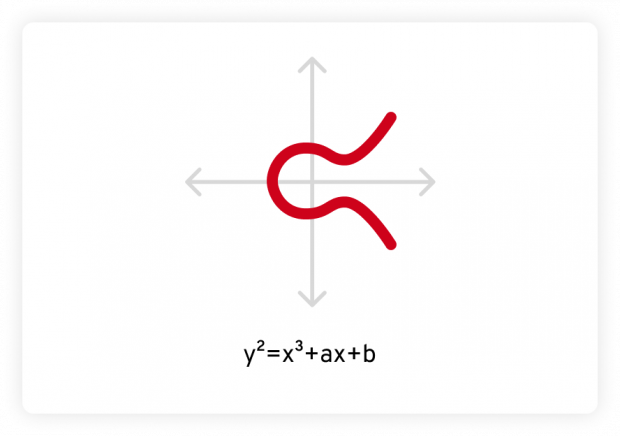
Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) is a variant of the Diffie–Hellman protocol using elliptic-curve cryptography. It has better computing performance and security than the classical DH algorithm that uses modular arithmetic. The elliptic curve is a curve described by the equation y2 = x3 + ax + b, and its plot is as follows:
ECDH key exchange steps are similar to the classical DH algorithm, but the calculation method is different:
- Agree on public parameters
Both parties (Alice and Bob) agree on the following elliptic curve parameters:- Elliptic Curve function EC,
- Generator point G,
- Generate private keys and public keys
- Private keys: Each party generates a private key. Alice gets
a, and Bob getsb. These private keys are kept secret and never shared. - Public keys: Each party computes their corresponding public key by performing elliptic curve point multiplication with the generator point. Alice gets
Pa = G•a, and Bob getsPb = G•b. - The multiplication operation
•here is the scalar multiplication of the elliptic curve, not the ordinary multiplication.
- Private keys: Each party generates a private key. Alice gets
- Exchange public keys
Alice and Bob send their public keys to each other. This exchange can be done over an insecure channel. - Each party computes the shared key
- Alice:
K = a•Pb = a•(b•G) - Bob:
K = b•Pa = b•(a•G) - According to the elliptic curve multiplication, the
Kcalculated by both parties is consistent.
- Alice:
- Sending messages encrypted by the shared key
ECDH 是采用 椭圆曲线密码 的 DH 算法,比起使用模运算的传统 DH 算法,它有更好的计算性能与安全性。椭圆曲线是由方程 y2 = x3 + ax + b 描述的曲线,其绘制图形如下:
ECDH 密钥交换步骤, 跟传统 DH 的逻辑一样,只是计算方法不同:
- 选择公开参数
双方选择一个椭圆曲线 EC 和基点 G. - 各自生成私钥和公钥
- 私钥: 每方生成一个随机私钥(一个大整数), Alice 的私钥为
a, Bob 的私钥为b. - 公钥: 通过基点 G 和私钥生成公钥, Alice 的公钥
Pa = G•a, Bob 的公钥为Pb = G•b. - 这里的点乘运算
•是椭圆曲线的标量乘法,不是普通的乘法.
- 私钥: 每方生成一个随机私钥(一个大整数), Alice 的私钥为
- 交换公钥
双方公开交换公钥,这个交换可以在不安全的通道上进行。 - 计算共享密钥
- Alice:
K = a•Pb = a•(b•G) - Bob:
K = b•Pa = b•(a•G) - 根据椭圆曲线的特性,双方计算出来的
K是一致的。
- Alice:
- 使用该共享密钥进行消息加密
Forward secrecy
RSA, as well as basic DH and ECDH, lack forward security. For DH and ECDH, we can choose to reselect a private key for each session, which can ensure forward security. This is called DHE and ECDHE. E here stands for Ephemeral, which means the private key is temporary and only used in one session.
Forward secrecy, 前向安全性。 如果服务器的长期私钥泄露,攻击者是否能解密过去的通信数据?(假定攻击者已经获得历史数据包)
为什么说 RSA, DH, ECDH 缺乏前向安全性,很重要的原因其实是因为在传统 TLS 的实际应用中,密钥交换过程中用到的服务端公钥私钥,就是服务器证书的公钥私钥。
以 TLS_RSA 为例,实际应用中就是将服务器的证书公钥作为 RSA 公钥,在客户端计算出共享密钥后,就使用这个公钥加密并发给服务器。所以如果此时服务器证书私钥(RSA 私钥)泄漏,攻击者就可以从历史流量数据中定位到这个发送共享密钥的数据包(client_key_exchange 包)并解密得到共享密钥,从而解密历史数据。
对于 DH, ECDH 可以在每次会话开始时(TLS 建立连接时)都重新选择私钥公钥,不跟服务器证书关联。这样即使服务器证书私钥泄漏,攻击者也无法计算出共享密钥。这就保证了前向安全,这就叫做 DHE, ECDHE。E 即 Ephemeral, 表示这个私钥是临时的。
Preventing MITM attacks
From the basic steps of key exchange mentioned above, we can see that they are all vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks, so in practical applications, certificate verification steps need to be added. I will show this in the TLS handshake following.
从上述密钥交换的基本步骤中,可以看出它们都容易被中间人攻击,所以在实际应用中,需要加上证书验证的步骤。这点我们可以在后面的 TLS 握手中看到。
TLS
TLS(Transport Layer Security) is the successor to SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), which has been largely deprecated since 1999, and even though the name SSL is used, it is actually TLS.
TLS only uses asymmetric encryption during the handshake phase and then uses a key exchange algorithm to negotiate a set of symmetric keys (called shared keys or session keys). It is these symmetric keys that are used in the data transfer phase (because they are more computationally efficient than asymmetric encryption).
TLS(Transport Layer Security,传输层安全协议)和 SSL(Secure Sockets Layer,安全套接字层协议)之间的关系是:TLS 是 SSL 的后继版本。SSL 在1999年后基本已经不再使用了,即使用到了 SSL 这个名称,其实内里也是 TLS。
TLS 只有在握手阶段是使用非对称加密,然后使用密钥交换算法协商出一组对称密钥(叫做 Shared Keys 或者 Session Keys, 或者叫 Key Block)。在数据传输阶段使用的就是这组对称密钥(因为计算效率比非对称加密高)。为什么说是一组 keys 呢?因为实际上它包括:
- client_write_MAC_key, 客户端用这个 key 计算 HMAC
- server_write_MAC_key, 服务端用这个 key 计算 HMAC
- client_write_key, 客户端用这个 key 加密数据,服务端用它来解密数据
- server_write_key, 服务端用这个 key 加密数据,客户端用它来解密数据
- 初始化向量 IV, 对称加密算法需要的一个值
- etc.
TLS Session vs. TLS Connection
- TLS Session
- Shared among multiple TLS connections, a session can have multiple connections (a connection can only correspond to one session). This is to support efficient session reuse without needing a new handshake for each connection.
- Contains a set of cryptographic parameters (especially the master secret).
- The life cycle is longer than the connection’s, and a session resumption mechanism exists.
- TLS Connection
- One connection is associated with one session. (One session can be associated with multiple connections).
- It contains session keys used for data transmission (session keys actually include Initialization Vectors, symmetric encryption keys, and MAC secrets).
- The life cycle is shorter and limited to one data transmission.
- It can be understood that each HTTPS request corresponds to a connection (without using connection reuse).
Pre-Master Secret, Master Secret, and Session Keys (预主密钥,主密钥与会话密钥)
[1] ECDHE 密钥交换
→ 得到 Pre-Master Secret(仅双方知道)
[2] 使用 预主密钥 计算 主密钥
Master Secret = PRF(Pre-Master Secret, "master secret", ClientRandom + ServerRandom)
[3] 使用 主密钥 计算 会话密钥 (Session Keys, 或叫 Key Block)
Key Block = PRF(Master Secret, "key expansion", ServerRandom + ClientRandom)
包括:
- client_write_MAC_key
- server_write_MAC_key
- client_write_key
- server_write_key
- IV 等其中 PRF (Pseudo-Random Function) 是密码学中的伪随机数函数。”master secret” 和 “key expansion” 实参是告诉这个函数我们需要输出什么结果。ClientRandom 和 ServerRandom 是在握手过程中交换的值 (Hello 阶段)。
- 预主密钥 由密钥交换算法生成,仅在握手期间存在,lifetime 短暂。
- 主密钥 由预主密钥通过随机数算法生成,在整个会话周期内都有效,lifetime 持久。
- 会话密钥 由主密钥通过随机数算法生成,通常在整个会话周期内有效,也有可能重新计算。
TLS1.2 handshake
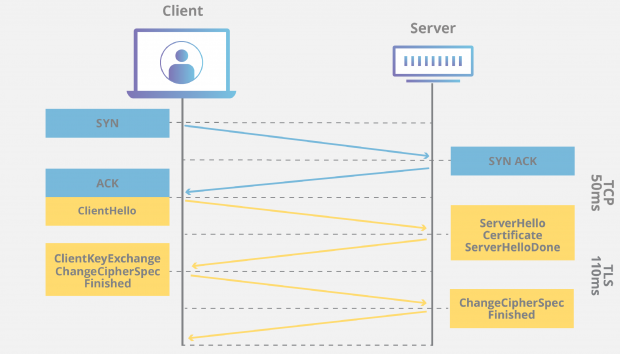
Step 1: Client Hello
- Client 发送 ClientHello 消息给服务器,包含:
- 客户端支持的 TLS 版本(如 TLS 1.2)。
- 客户端支持的加密套件列表(如 AES、RSA、ECDHE 等)。
- 一个随机数(
Client Random)用于后续的主密钥生成。 - 支持的压缩方法和其他扩展选项。
- say hello 阶段不加密
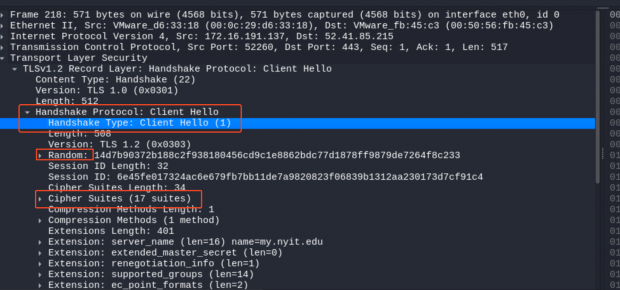
Step 2: Server Hello (and Key Exchange)
- 服务器发回 ServerHello 消息,包含:
- 服务器选择的 TLS 版本(例如 TLS 1.2)。
- 选择的加密套件(根据客户端提供的选项)。
- 另一个随机数(
Server Random),用于主密钥生成。 - 服务器的数字证书,用于身份验证,证书中包含服务器的公钥。(certificate + pubkey + signature)
- say hello 阶段不加密
- 服务器发送 ServerKeyExchange 消息 (可选, 使用 DHE/ECDHE 密钥交换的才会有)
- 包含 DHE/ECDHE 密钥交换所需的公开参数:
- 如果是 DHE, 则由服务端指定 大素数
p和 生成元g。如果是 ECDHE, 则由服务端指定椭圆曲线EC和基点G - 还包含服务端计算的 DHE/ECDHE 公钥
- 使用 服务器证书的私钥(不是 DH/ECDH 私钥!) 对上述数据进行签名,防止被中间人篡改
- 如果是 DHE, 则由服务端指定 大素数
- 如果使用 RSA 密钥交换,服务器不需要发送 ServerKeyExchange 包。因为客户端在后面可以独立生成 预主密钥。
- 如果使用传统 DH/ECDH 密钥交换(或者叫静态 DH/ECDH),也不需要 ServerKeyExchange 包。因为他们的公开参数以及公钥都会放在服务器证书中下发(SubjectPublicKeyInfo 键)。
- 包含 DHE/ECDHE 密钥交换所需的公开参数:
如果服务器要求客户端认证(如双向 TLS),它还会请求客户端的证书(certificate_request 包)。
服务器下发的证书,是一个“证书链”。通常包括服务器证书 + 中间 CA 证书,有可能还包含 Root CA 证书 (理论上 Root CA 证书应该是预安装在客户系统或者浏览器里的,不需要服务器下发)。
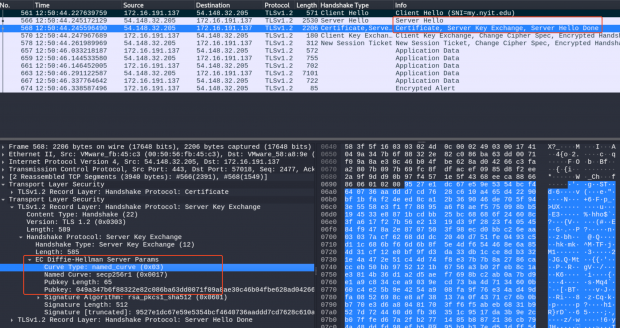
Step 3: Client Verification, Key Exchange, Finished
- 客户端验证服务器证书 (certificate_verify 包)
- 客户端根据 key exhange 算法生成预主密钥,发送 client_key_exchange 包
- 如果使用的是 RSA 密钥交换,客户端独立生成预主密钥后使用服务器公钥加密并放在 client_key_exchange 包中发送给服务器。
- 如果使用的是 Diffie-Hellman 密钥交换,则客户端根据服务端给的公开参数计算出 DH/ECDH 公钥,放在 client_key_exchange 包中发送给服务器。
- 根据
Client Random、Server Random和 预主密钥 生成 主密钥(Master secret),然后再生成 session keys 用于对数据传输进行加密。 - 所有密钥都计算完后,发送 change_cipher_spec 包,告诉对方”接下来我可要开始加密传输了啊。”(所以 ChangeCipherSpec 包的内容其实只有一个
0x01,就是一个通知) - 加密发送 Finished 包给服务器。(Finished 包的数据是一些校验值,对方必须解密并且进行验证)
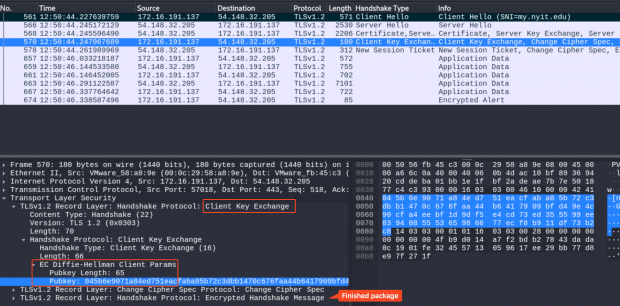
Step 4: Server Finished
- 服务端根据客户端提交的 ClientKeyExchange 信息计算出各种密钥(预主密钥,主密钥,会话密钥)
- 服务端发回 ChangeCIpherSpec 包,通知”我接下来也要开始加密了啊”
- 服务端发回加密的 Finished 包
- 握手完成!🎉
TLS1.3 handshake
- TLS 1.3 在发送 hello 包的时候就已经包含了密钥交换的一些安全参数,从而减少握手的步骤。
- TLS 1.3 不再支持 RSA 密钥交换方式,只支持 DH 系的密钥交换(DH 或者 ECDHE)。
- TLS 1.3 握手只需要 1 个 RTT(Round trip time, 一来一回),虽然客户端要在第 1.5 个 RTT 才开始发送加密消息。TLS 1.2 握手需要 2 个 RTT。
Step 1: Client Hello + Client Cryptographic Parameters
- 客户端发送 Client Hello 包,其中包含:
- 客户端随机数(ClientHello.random)
- 支持的加密套件(Cipher suites)
- 支持的密钥交换算法,以及所需的安全参数(包括 client key_share, 可以简单理解为就是 DH 方法的公钥)
Step 2: Server Hello + Server Cryptographic Parameters
- 服务器回应 Server Hello 包,其中包含:
- 服务器随机数
- 服务器选中的加密套件 (Cipher suites)
- 服务器的 key_share (服务器的 DH 公钥)
- 服务器计算出共享密钥,发送 change cipher spec 包,
- 然后服务器就开始使用共享密钥加密并发送消息了(包括 Certificate, Finished 都在加密包里)。 (我理解是 TLS 1.3 这里的共享密钥包括了,类似 TLS 1.2 中的 主密钥,session keys 的所有密钥,当然可能不再叫这些名字了。)
Step 3: Client Calculate Keys and Finished
- 客户端计算出共享密钥,发送 change cipher spec 包,然后就开始使用共享密钥加密并发送消息。
Cipher suite naming scheme (加密套件的命名规则)
Each cipher suite has a unique name used to identify it and describe its algorithmic contents. The naming of cipher suites usually follows certain rules and usually consists of the following segments, separated by underscores:
[protocol]_[key exchange algorithm]_[authentication algorithm]_[session encryption algorithm]_[message authentication algorithm]Take TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 for example.
- TLS
Defines the protocol this cipher suite is for; it will usually be TLS. - ECDHE
Indicates the key exchange algorithm being used. - RSA
Authentication mechanism during the handshake.
比如握手过程中,服务器下发 ECDHE 公开参数,就必须用服务器证书的 RSA 私钥进行签名 (RSA 加密哈希值),然后客户端使用证书公钥进行签名验证 (RSA 解密)。 - AES_128_GCM
Session cipher algorithm. After the handshake, the session communication between the two parties will be encrypted using a symmetric encryption algorithm. - SHA256
Indicates the message authentication algorithm used to generate a MAC(Message Authentication Code) and authenticate a message.
References
- Wikipedia contributors. (2024a, May 5). Key exchange. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Key_exchange
- Wikipedia contributors. (2024b, September 5). Cipher suite. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cipher_suite
- Wikipedia contributors. (2024c, October 12). Diffie–Hellman key exchange. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffie%E2%80%93Hellman_key_exchange
- Wikipedia contributors. (2024d, October 14). Elliptic-Curve Diffie–Hellman. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elliptic-curve_Diffie%E2%80%93Hellman
- 结城浩. (2016). 图解密码技术: 第3版.