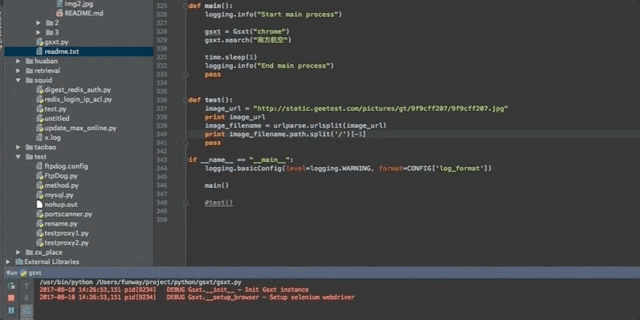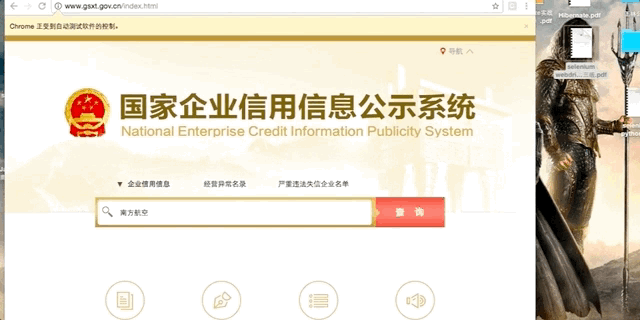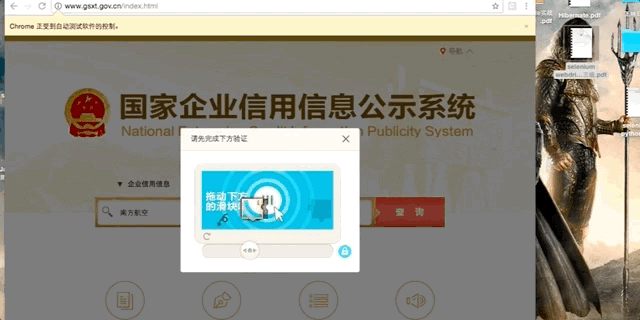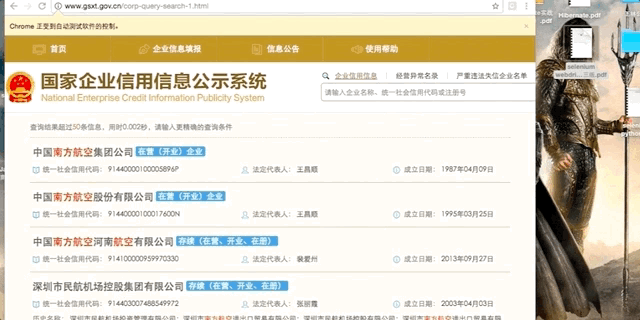
最近有个项目需要爬取“国家企业信用信息公示系统”的数据,在该网站点击搜索按钮时,会弹出极验(geetest)的拖动式验证码。
遂一番google之,发现果然有哥们已经破解了这套验证码系统,甚至放出源码来了。学以致用。
原理很简单,首先定位缺口的位置,然后驱动浏览器将按钮移动到该位置。至于如何定位缺口位置,其实这个验证图是分上下两张的,底图是完整图,上一层则是有缺口的图,另外这两张图都是打散的,需要先还原出原图,然后再逐像素对比两张图片就可以得到缺口位置。移动按钮看似简单,但如果只是简单的将按钮设置到目标位置,极验后台会返回“怪物吃了拼图”,因为该验证码系统会将按钮的移动轨迹提交到极验后台,并验证该轨迹是否像一个人类的行为,所以我们需要尽可能模拟出人类的拖动行为。
代码示例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
import time
import random
import re
import requests
import urlparse
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
"""
程序目的:
访问国家企业信用信息公示系统(http://www.gsxt.gov.cn/index.html),
输入查询关键字,
破解弹出的极验验证码系统(geetest)并搜索,最后获取搜索结果。
"""
VERSION = "1.0"
CONFIG = {
'log_format': "%(asctime)s pid[%(process)d] %(levelname)7s %(name)s.%(funcName)s - %(message)s",
'save_temp_file': False, }
class Gsxt(object):
""""""
def __init__(self, driver):
"""构造函数"""
super(Gsxt, self).__init__()
self.logger = logging.getLogger(self.__class__.__name__)
self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
self.logger.debug("Init Gsxt instance")
self.browser = None
self.__setup_browser(driver)
pass
def __del__(self):
"""析构函数"""
self.logger.debug("Del Gsxt instance")
if self.browser is not None:
self.browser.quit()
pass
def __setup_browser(self, driver):
"""装载浏览器驱动"""
self.logger.debug("Setup selenium webdriver")
driver = driver.lower()
if "phantomjs" == driver:
self.browser = webdriver.PhantomJS()
elif "chrome" == driver:
self.browser = webdriver.Chrome()
elif "firefox" == driver:
raise Exception("请不要使用firefox,因为geckodriver暂时有点功能不全!凸(-。-;")
else:
raise Exception("不识别的浏览器驱动")
# 设置打开页面超时时间(但这对firefox的geckodriver 0.13.0版本无效,不知道后续改进没有)
self.browser.set_page_load_timeout(8)
# 设置查询dom的隐式等待时间(影响find_element_xxx,find_elements_xxx)
self.browser.implicitly_wait(10)
pass
def search(self, keyword):
"""
Args:
keyword: 要搜索的关键字
Returns:
"""
if type(keyword) is str:
keyword = keyword.decode('utf-8')
self.logger.debug(u"准备搜索: %s", keyword)
# 打开搜索页面
self.browser.get("http://www.gsxt.gov.cn/index.html")
# 输入关键字
dom_input_keyword = self.browser.find_element_by_id("keyword")
dom_input_keyword.send_keys(keyword)
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.3, 1.0))
# 点击搜索按钮
dom_btn_query = self.browser.find_element_by_id("btn_query")
dom_btn_query.click()
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.8, 1.5))
flag_success = False
while not flag_success:
# 下载完整的验证图
image_full_bg = self.get_image("gt_cut_fullbg_slice")
# 下载有缺口的验证图
image_bg = self.get_image("gt_cut_bg_slice")
# 对比两张验证图,获得缺口的位置(x_offset)
diff_x = self.get_diff_x(image_full_bg, image_bg)
self.logger.debug(u"缺口位置x_offset = %s", diff_x)
# 根据缺口位置计算移动轨迹
track = self.get_track(diff_x)
# 移动滑块
result = self.simulate_drag(track)
# 判断滑动验证的结果
if u"通过" in result:
flag_success = True
pass
elif u"吃" in result:
self.logger.debug(u"准备重试")
time.sleep(5)
pass
else:
self.logger.warn(u"未知结果")
break
pass
# 获取搜索结果
if flag_success:
time.sleep(random.uniform(0.8, 1.5))
# do sth
pass
pass
def get_image(self, class_name):
"""
下载并还原极验的验证图
Args:
class_name: 验证图所在的html标签的class name
Returns:
返回验证图
Errors:
IndexError: list index out of range. ajax超时未加载完成,导致image_slices为空
"""
self.logger.debug(u"获取验证图像: class='%s'", class_name)
image_slices = self.browser.find_elements_by_class_name(class_name)
if len(image_slices) == 0:
self.logger.warn(u"无法找到class='%s'的标签", class_name)
div_style = image_slices[0].get_attribute('style')
self.logger.debug(u"div style=%s", div_style)
# 获取图像url
image_url = re.findall("background-image: url\(\"(.*)\"\); background-position: (.*)px (.*)px;",
div_style)[0][0]
# chrome浏览器得到的验证图是webp格式,其他浏览器都是jpg格式。
image_url = image_url.replace("webp", "jpg")
self.logger.debug(u"验证图像url: %s", image_url)
image_filename = urlparse.urlsplit(image_url).path.split('/')[-1]
# 获取图像的每个切片位置
location_list = list()
for image_slice in image_slices:
location = dict()
location['x'] = int(re.findall("background-image: url\(\"(.*)\"\); background-position: (.*)px (.*)px;",
image_slice.get_attribute('style'))[0][1])
location['y'] = int(re.findall("background-image: url\(\"(.*)\"\); background-position: (.*)px (.*)px;",
image_slice.get_attribute('style'))[0][2])
self.logger.debug(location)
location_list.append(location)
# 通过request请求获取验证图
headers = {"Host": "static.geetest.com",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/56.0.2924.87 Safari/537.36"}
response = requests.get(image_url, headers=headers)
# 构造Image类型的验证图
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
if CONFIG['save_temp_file']:
self.logger.debug(u"保存验证图像(原图): %s", image_filename)
image.save(image_filename)
# 还原验证图
image = self.recover_image(image, location_list)
if CONFIG['save_temp_file']:
self.logger.debug(u"保存验证图像(复原图): %s", "re_"+image_filename)
image.save("re_" + image_filename)
return image
def recover_image(self, image, location_list):
"""
还原验证图像
Args:
image: 打乱的验证图像(PIL.Image数据类型)
location_list: 验证图像每个碎片的位置
Returns:
还原过后的图像
"""
self.logger.debug(u"开始还原验证图像...")
new_im = Image.new('RGB', (260, 116))
im_list_upper = []
im_list_down = []
for location in location_list:
if location['y'] == -58:
im_list_upper.append(image.crop((abs(location['x']), 58, abs(location['x']) + 10, 166)))
if location['y'] == 0:
im_list_down.append(image.crop((abs(location['x']), 0, abs(location['x']) + 10, 58)))
x_offset = 0
for im in im_list_upper:
new_im.paste(im, (x_offset, 0))
x_offset += im.size[0]
x_offset = 0
for im in im_list_down:
new_im.paste(im, (x_offset, 58))
x_offset += im.size[0]
return new_im
def get_diff_x(self, image1, image2):
"""
计算验证图的缺口位置(x轴)
两张原始图的大小都是相同的260*116,那就通过两个for循环依次对比每个像素点的RGB值,
如果RGB三元素中有一个相差超过50则就认为找到了缺口的位置
Args:
image1: 图像1
image2: 图像2
Returns:
x_offset
"""
for x in range(0, 260):
for y in range(0, 116):
if not self.__is_similar(image1, image2, x, y):
return x
def __is_similar(self, image1, image2, x_offset, y_offset):
"""
判断image1, image2的[x, y]这一像素是否相似,如果该像素的RGB值相差都在50以内,则认为相似。
Args:
image1: 图像1
image2: 图像2
x_offset: x坐标
y_offset: y坐标
Returns:
boolean
"""
pixel1 = image1.getpixel((x_offset, y_offset))
pixel2 = image2.getpixel((x_offset, y_offset))
for i in range(0, 3):
if abs(pixel1[i] - pixel2[i]) >= 50:
return False
return True
def get_track(self, x_offset):
"""
根据缺口位置x_offset,仿照手动拖动滑块时的移动轨迹。
手动拖动滑块有几个特点:
开始时拖动速度快,最后接近目标时会慢下来;
总时间大概1~3秒;
但是现在这个简单的模拟轨迹成功率并不高,只能说能用。我并不懂关于机器学习的知识,但我想如果能用上的话应该会好一些
Args:
x_offset: 验证图像的缺口位置,亦即滑块的目标地址
Returns:
返回一个轨迹数组,数组中的每个轨迹都是[x,y,z]三元素:x代表横向位移,y代表竖向位移,z代表时间间隔
[[x1,y1,z1], [x2,y2,z2], ...]
"""
track = list()
# 实际上滑块的起始位置并不是在图像的最左边,而是大概有6个像素的距离,所以滑动距离要减掉这个长度
length = x_offset - 6
total_time = 0
x = random.randint(1, 3)
while length - x >= 5:
track.append([x, 0, 0])
length = length - x
x = random.randint(1, 3)
total_time += track[-1][2]
for i in range(length):
track.append([1, 0, random.randint(10, 20)/100.0])
total_time += track[-1][2]
self.logger.debug(u"计算出移动轨迹; %s", track)
self.logger.debug(u"预计耗时: %s", total_time)
return track
def simulate_drag(self, track):
"""
根据移动轨迹,模拟拖动极验的验证滑块
Args:
track: 移动轨迹
Returns:
"""
self.logger.debug(u"开始模拟拖动滑块")
# 获得滑块元素
dom_div_slider = self.browser.find_element_by_class_name("gt_slider_knob")
self.logger.debug(u"滑块初始位置: %s", dom_div_slider.location)
ActionChains(self.browser).click_and_hold(on_element=dom_div_slider).perform()
for x, y, z in track:
self.logger.debug(u"位移: (%s, %s), 等待%s秒", x, y, z)
ActionChains(self.browser).move_to_element_with_offset(
to_element=dom_div_slider,
xoffset=x+22,
yoffset=y+22).perform()
self.logger.debug(u"滑块当前位置: %s", dom_div_slider.location)
time.sleep(z)
pass
time.sleep(0.2)
ActionChains(self.browser).release(on_element=dom_div_slider).perform()
time.sleep(1)
dom_div_gt_info = self.browser.find_element_by_class_name("gt_info_text")
self.logger.debug(u"拖动结果【%s】", dom_div_gt_info.text)
return dom_div_gt_info.text
def main():
logging.info("Start main process")
gsxt = Gsxt("chrome")
gsxt.search("南方航空")
time.sleep(1)
logging.info("End main process")
pass
def test():
image_url = "http://static.geetest.com/pictures/gt/9f9cff207/9f9cff207.jpg"
print image_url
image_filename = urlparse.urlsplit(image_url)
print image_filename.path.split('/')[-1]
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARNING, format=CONFIG['log_format'])
main()
#test()
参考: