Official Manual
Nmap 7.95SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Usage: nmap [Scan Type(s)] [Options] {target specification}
TARGET SPECIFICATION:
Can pass hostnames, IP addresses, networks, etc.
Ex: scanme.nmap.org, microsoft.com/24, 192.168.0.1; 10.0.0-255.1-254
-iL <inputfilename>: Input from list of hosts/networks
-iR <num hosts>: Choose random targets
--exclude <host1[,host2][,host3],...>: Exclude hosts/networks
--excludefile <exclude_file>: Exclude list from file
HOST DISCOVERY:
-sL: List Scan - simply list targets to scan
-sn: Ping Scan - disable port scan
-Pn: Treat all hosts as online -- skip host discovery
-PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: TCP SYN, TCP ACK, UDP or SCTP discovery to given ports
-PE/PP/PM: ICMP echo, timestamp, and netmask request discovery probes
-PO[protocol list]: IP Protocol Ping
-n/-R: Never do DNS resolution/Always resolve [default: sometimes]
--dns-servers <serv1[,serv2],...>: Specify custom DNS servers
--system-dns: Use OS's DNS resolver
--traceroute: Trace hop path to each host
SCAN TECHNIQUES:
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM: TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans
-sU: UDP Scan
-sN/sF/sX: TCP Null, FIN, and Xmas scans
--scanflags <flags>: Customize TCP scan flags
-sI <zombie host[:probeport]>: Idle scan
-sY/sZ: SCTP INIT/COOKIE-ECHO scans
-sO: IP protocol scan
-b <FTP relay host>: FTP bounce scan
PORT SPECIFICATION AND SCAN ORDER:
-p <port ranges>: Only scan specified ports
Ex: -p22; -p1-65535; -p U:53,111,137,T:21-25,80,139,8080,S:9
--exclude-ports <port ranges>: Exclude the specified ports from scanning
-F: Fast mode - Scan fewer ports than the default scan
-r: Scan ports sequentially - don't randomize
--top-ports <number>: Scan <number> most common ports
--port-ratio <ratio>: Scan ports more common than <ratio>
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
--version-intensity <level>: Set from 0 (light) to 9 (try all probes)
--version-light: Limit to most likely probes (intensity 2)
--version-all: Try every single probe (intensity 9)
--version-trace: Show detailed version scan activity (for debugging)
SCRIPT SCAN:
-sC: equivalent to --script=default
--script=<Lua scripts>: <Lua scripts> is a comma separated list of
directories, script-files or script-categories
--script-args=<n1=v1,[n2=v2,...]>: provide arguments to scripts
--script-args-file=filename: provide NSE script args in a file
--script-trace: Show all data sent and received
--script-updatedb: Update the script database.
--script-help=<Lua scripts>: Show help about scripts.
<Lua scripts> is a comma-separated list of script-files or
script-categories.
OS DETECTION:
-O: Enable OS detection
--osscan-limit: Limit OS detection to promising targets
--osscan-guess: Guess OS more aggressively
TIMING AND PERFORMANCE:
Options which take <time> are in seconds, or append 'ms' (milliseconds),
's' (seconds), 'm' (minutes), or 'h' (hours) to the value (e.g. 30m).
-T<0-5>: Set timing template (higher is faster)
--min-hostgroup/max-hostgroup <size>: Parallel host scan group sizes
--min-parallelism/max-parallelism <numprobes>: Probe parallelization
--min-rtt-timeout/max-rtt-timeout/initial-rtt-timeout <time>: Specifies
probe round trip time.
--max-retries <tries>: Caps number of port scan probe retransmissions.
--host-timeout <time>: Give up on target after this long
--scan-delay/--max-scan-delay <time>: Adjust delay between probes
--min-rate <number>: Send packets no slower than <number> per second
--max-rate <number>: Send packets no faster than <number> per second
FIREWALL/IDS EVASION AND SPOOFING:
-f; --mtu <val>: fragment packets (optionally w/given MTU)
-D <decoy1,decoy2[,ME],...>: Cloak a scan with decoys
-S <IP_Address>: Spoof source address
-e <iface>: Use specified interface
-g/--source-port <portnum>: Use given port number
--proxies <url1,[url2],...>: Relay connections through HTTP/SOCKS4 proxies
--data <hex string>: Append a custom payload to sent packets
--data-string <string>: Append a custom ASCII string to sent packets
--data-length <num>: Append random data to sent packets
--ip-options <options>: Send packets with specified ip options
--ttl <val>: Set IP time-to-live field
--spoof-mac <mac address/prefix/vendor name>: Spoof your MAC address
--badsum: Send packets with a bogus TCP/UDP/SCTP checksum
OUTPUT:
-oN/-oX/-oS/-oG <file>: Output scan in normal, XML, s|<rIpt kIddi3,
and Grepable format, respectively, to the given filename.
-oA <basename>: Output in the three major formats at once
-v: Increase verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect)
-d: Increase debugging level (use -dd or more for greater effect)
--reason: Display the reason a port is in a particular state
--open: Only show open (or possibly open) ports
--packet-trace: Show all packets sent and received
--iflist: Print host interfaces and routes (for debugging)
--append-output: Append to rather than clobber specified output files
--resume <filename>: Resume an aborted scan
--noninteractive: Disable runtime interactions via keyboard
--stylesheet <path/URL>: XSL stylesheet to transform XML output to HTML
--webxml: Reference stylesheet from Nmap.Org for more portable XML
--no-stylesheet: Prevent associating of XSL stylesheet w/XML output
MISC:
-6: Enable IPv6 scanning
-A: Enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute
--datadir <dirname>: Specify custom Nmap data file location
--send-eth/--send-ip: Send using raw ethernet frames or IP packets
--privileged: Assume that the user is fully privileged
--unprivileged: Assume the user lacks raw socket privileges
-V: Print version number
-h: Print this help summary page.
EXAMPLES:
nmap -v -A scanme.nmap.org
nmap -v -sn 192.168.0.0/16 10.0.0.0/8
nmap -v -iR 10000 -Pn -p 80
SEE THE MAN PAGE (https://nmap.org/book/man.html) FOR MORE OPTIONS AND EXAMPLESExamples
默认扫描
nmap 192.168.1.1默认扫描会执行以下行为:- (ARP) ping scan, 确认目标主机是否在线,如果不在线则中断后续操作。 nmap 会根据 IP 自动使用 ARP ping (局域网) 或者 ICMP ping (公网)。
- Parallel DNS resolution, 反向 DNS 查询,查询主机名
- SYN Stealth Scan, 使用 TCP SYN 半连接扫描,扫描目标主机的端口
- 默认只扫描前 1000 号端口
- 所以,它等效于
nmap 192.168.1.1 -sS -p 1-1000
快速主机发现
nmap -sn 192.168.1.1/24主机发现扫描nmap -sn -n -v 192.168.1.1/24快速主机发现扫描-sn表示只进行主机扫描(ping scan / ping sweep),不进行端口扫描 (其中 s 表示扫描 scan, n 表示 not port。但是要注意-sn这种两个字母连在一起的参数是不能拆开的!)-n表示禁用 DNS 查询,这样才能加速主机发现-v表示输出详细信息
跳过主机发现
nmap host -Pn跳过主机发现- 如果不定义该参数,所有的扫描默认都会先执行 ping 扫描来确认主机是否在线,如果不在线就会中断后续操作。
端口扫描
指定端口
-p 80指定扫描80端口-p 80, 443指定扫描两个端口-p 80-8080指定端口范围-p-全部端口
结果解读
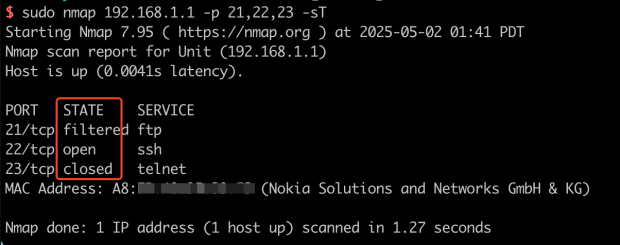
端口扫描的结果会有三种状态:
- open 表示目标端口开放连接
- closed 表示目标端口返回
RST包 - filtered 表示目标端口什么都没有返回,请求包可能被 iptables, 防火墙或者其他安全设备 drop 掉了 (如果不是使用完整的
-sT全连接扫描,很容易被识别为异常直接 drop 掉)
扫描方式
Note: –sS, sA, sF, sX, sN 这些异常的扫描数据包很有可能被现代操作系统或者防火墙识别,并直接 drop 或者 RST。所以很难准确判断端口状态。
nmap -sS hostTCP SYN 扫描(半连接扫描)- 只发送
SYN包,收到目标返回的SYN/ACK包后立即发RST包中止握手 - 需要 root/sudo 权限
- 只发送
nmap -sT hostTCP 全连接扫描- 完整的 TCP 三次握手全连接:
- 客户端发送
SYN包,请求连接 - 服务器返回
SYN/ACK包,确认请求并发送自己的 SYN 号 - 客户端发送
ACK包,确认连接建立
- 客户端发送
- 完整的 TCP 三次握手全连接:
nmap -sA hostACK 扫描- 并不用于判断端口是否 open,而是用来判断端口是否被防火墙过滤(filtered / unfiltered)
- 因为正常主机一开始收到
ACK包,会返回RST表示异常请求,需要 reset,这时 nmap 就会判断 unfiltered - 防火墙如果遇到异常的
ACK包,会直接 drop 掉,不会返回RST,这时 nmap 就会判断 filtered - 但是我觉得这其实并不准确,因为不同系统或者防火墙对于
ACK包的响应可能有差异
nmap -sX hostXmax 扫描- 发送一个特殊的 TCP 包,其包头的
Flags字段为FIN + PSH + URG(就像圣诞树一样亮了很多灯🎄) - 但实际上这种异常的包很容易就被防火墙 drop 掉了。。。所以也没啥意义现在
- 发送一个特殊的 TCP 包,其包头的
nmap -sI zombie-host target-hostIdle 扫描- 利用僵尸主机进行扫描目标主机,不暴露自身
- 首先确认僵尸主机有 IPID 漏洞,即它的 IP 数据包的 ID 是连续的
- 然后向僵尸主机发送
SYN/ACK包,获取其当前的 IP ID = N。(为什么发送SYN/ACK包呢,因为SYN/ACK包是 TCP 三次握手的第二个包,而僵尸主机并没有发起过第一个SYN包,那么当它收到这个SYN/ACK包之后,就会返回一个RST包,而不会建立 TCP 连接。) - 再伪造成僵尸主机,向目标主机的目标端口发送
SYN/ACK数据包。- 如果目标端口在线,目标主机就会回复数据给僵尸主机,导致僵尸主机回复它
RST并且 IP ID = N+1。
- 如果目标端口在线,目标主机就会回复数据给僵尸主机,导致僵尸主机回复它
- 最后再向僵尸主机发送
SYN/ACK包,检查僵尸主机回复的数据包。- 如果 IP ID = N+2,那么说明目标主机端口在线。
- 如果 IP ID = N+1,那么说明目标主机端口不在线。
nmap -v -O --script ipidseq host确认 host 是否有 IPID seq 漏洞 (是否可以用来做僵尸主机)-O探测目标主机操作系统--script ipidseq表示使用 ipidseq 脚本
NSE (Nmap Script Engine)
nmap host --script=script_name指定要使用的脚本名nmap host --script="smb-*"使用 wildcard 匹配脚本名
扫描结果保存
-oN <filename>Normal text output-oG <filename>Grepable output-oX <filename>XML output-oA <filename>Generate All of the three types of files above